|
The True Calendar | ||||||||
|
The sun, moon, and stars, function together as a giant
clock. The Moon is a part of the measure of time.  The new month begins after the conjunction, as the moon begins to gather light. The conjunction happens at the same moment in time no matter where a person is on the earth. |
Moon Phases When is the conjunction?
|
||||||||
|
Notice
the consistent pattern that
every
Solar
Eclipse
happens on a
New Moon,
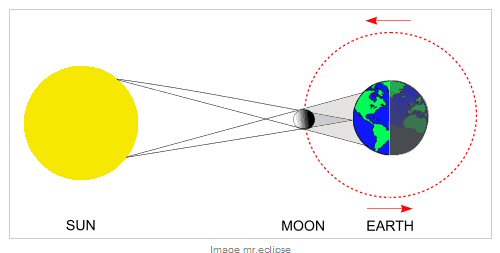
when the Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun, and
casts its shadow on the Earth. An eclipse of the Sun
can happen only when the Moon is new, and thus lies on
the Sun-side of the Earth. If the Moon's orbit lay in
the same plane as that of the Earth, there would be an
eclipse every month. However, because the lunar orbit
is tilted at an angle of about five degrees, most
times the
New Moon
passes unseen either above or below the Sun in the sky
and no eclipse is seen on Earth.
The Feast of Passover is kept after the Spring Equinox. When the Full Moon of March falls before the Spring Equinox (moment when the Sun is positioned directly over the Earth's equator), the celebration of Pesach moves forward to the next month which makes a 13-month year. There is no direct command in the Torah to add an additional month to the outgoing year. However because in each year the cycle of the Moon falls behind the cycle of the Sun by 10 days; it is necessary about every three years to adjust by approximately 28 - 30 days the Calendar to keep it in line with the Sun which regulates the four seasons.
In the month of
Xanthicus, which is by us called Nisan, and is the
beginning of our year, on the fourteenth day of the
lunar month,
when the sun is in Aries,
(for in this month it was that we were delivered from
bondage under the Egyptians,) the law ordained that we
should every year slay that sacrifice which I before
told you we slew when we came out of Egypt, and which
was called the Passover; and so we do celebrate this
passover in companies, leaving nothing of what we
sacrifice till the day following.
An eclipse
of the Moon (or lunar eclipse) can
only occur
at
Full Moon,
and only if the Moon passes through some portion of
Earth's shadow. That shadow is actually composed of
two cone-shaped components, one nested inside the
other. The outer or penumbral shadow is a zone where
the Earth blocks part but not all of the Sun's rays
from reaching the Moon. In contrast, the inner or
umbral shadow is a region where the Earth blocks
all direct sunlight from reaching the Moon.
Astronomers
recognize three basic types of lunar eclipses:
|
1ST New Moon on 30
March
2014 at 1:45 P.m. E S T Full Moon 15 April 2014 2:42 A.m. EST Total Lunar Eclipse (Passover) (Blood red) 2ND New Moon on 29 April 2014 1:14 A.m. EST Annular Solar Eclipse 3RD New Moon on 28 May 2014 at 1:40 P.m. E S T 4TH New Moon on 27 JuNe 2014 at 3:09 A.m. E S T 5TH New Moon on 26 JULy 2014 at 5:42 p.m. E S T 6TH New Moon on 25 AUGUST 2014 at 9:13 A.m. E S T 7TH New Moon on 24 September 2014 at 1:14 A.m. E S T Full Moon 8 Oct 2014 5:51 A.m. EST Total Lunar Eclipse Sukkoth (Blood red) 8TH New Moon on 23 Oct 2014 at 4:57 P.m. E S T Partial Solar Eclipse 9TH New Moon on 22 November 2014 at 7:32 a.m. E S T 10TH New Moon on 21 December 2014 at 8:36 P.m. E S T 11TH New Moon on 20 January 2015 at 8:14 a.m. E S T 12TH New Moon on 18 Feb 2015 at 6:47 p.m. E S T |
||||||||
|
1ST New Moon on
20 Mar 2015 at 4:36 A.m. E S
T Total Solar Eclipse Full Moon 4 April 2015 10:44 P.m. EST Partial Lunar Eclipse (Passover) (Blood red) 2ND New Moon on 18 APRIL 2015 at 1.37 P.m. E S T 3RD New Moon on 17 MAY 2015 at 11:13 P.m. E S T 4TH New Moon on 16 JuNE 2015 at 9:05 A.m. E S T 5TH New Moon on 15 JULY 2015 at 8:24 p.m. E S T 6TH New Moon on 14 AUGUST 2015 at 9:54 A.m. E S T 7TH New Moon on 13 SepT 2015 1:41 A.m. E S T Partial Solar Eclipse Full Moon 27 SEPT 2015 +/- 9:50 P.m. EST Sukkoth (Blood red) ( 28 SEPT 2015; 3:48 A.M. visible Jerusalem) Total Lunar Eclipse 8TH New Moon on 12 October 2015 at 7:06 P.m. E S T 9TH New Moon on 11 November 2015 at 12:47 P.m. E S T 10TH New Moon on 11 December 2015 at 5:29 A.m. E S T |
|||||||||
Solar eclipsesare of three types: total, partial and annular. The type seen depends on what part of the Moon's shadow passes over the observation point and the distance between the Earth and the Moon at the time of the eclipse.
An eclipse of the Sun occurs
when the Earth passes through the Moon's shadow. Total solar eclipses are the result of the Sun and the Moon being almost exactly the same angular size as we see them from Earth During a total eclipse the Moon covers the bright disk of the Sun, but little or none of the surrounding space. This allows us to see features of the Sun that would otherwise be invisible, except from outer space. These include the corona, which stretches out from the Sun in all directions, and solar prominences - large arch-shaped structures observable in the corona.
| |||||||||
|
3 |
|||||||||